Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

It is important to know that the equation listed above is a summary equation.
Cellular respiration formula explained. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration formula is the collective term for a number of different processes which convert biochemical energy derived from nutrients into a molecule called adenosine triphosphate atp the form of usable chemical energy needed to drive cellular processes. Adenosine triphosphate chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
This is the balanced equation that yields energy. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is.
ENE1L5 EK ENE1L7 EK Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. This type of respiration is common in most of the. In summary cellular respiration is a process that cells use to make energy.
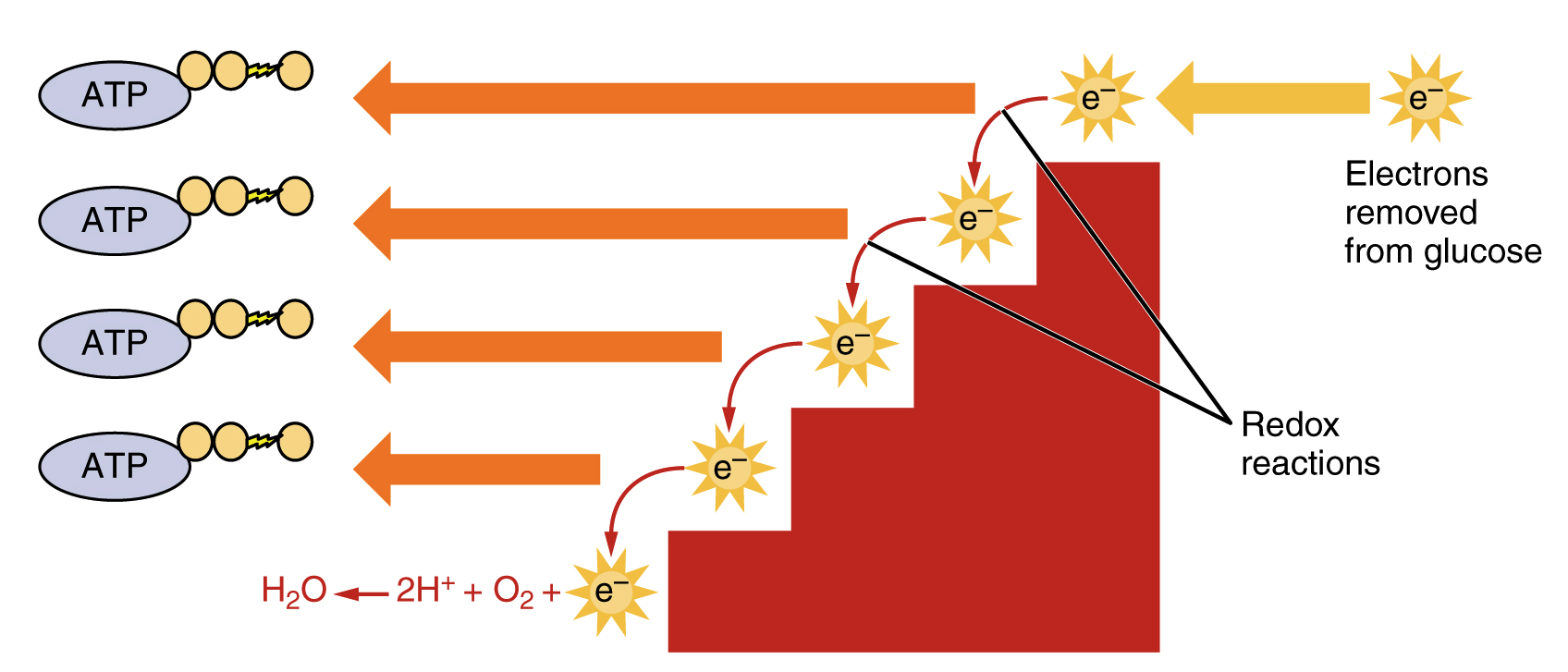
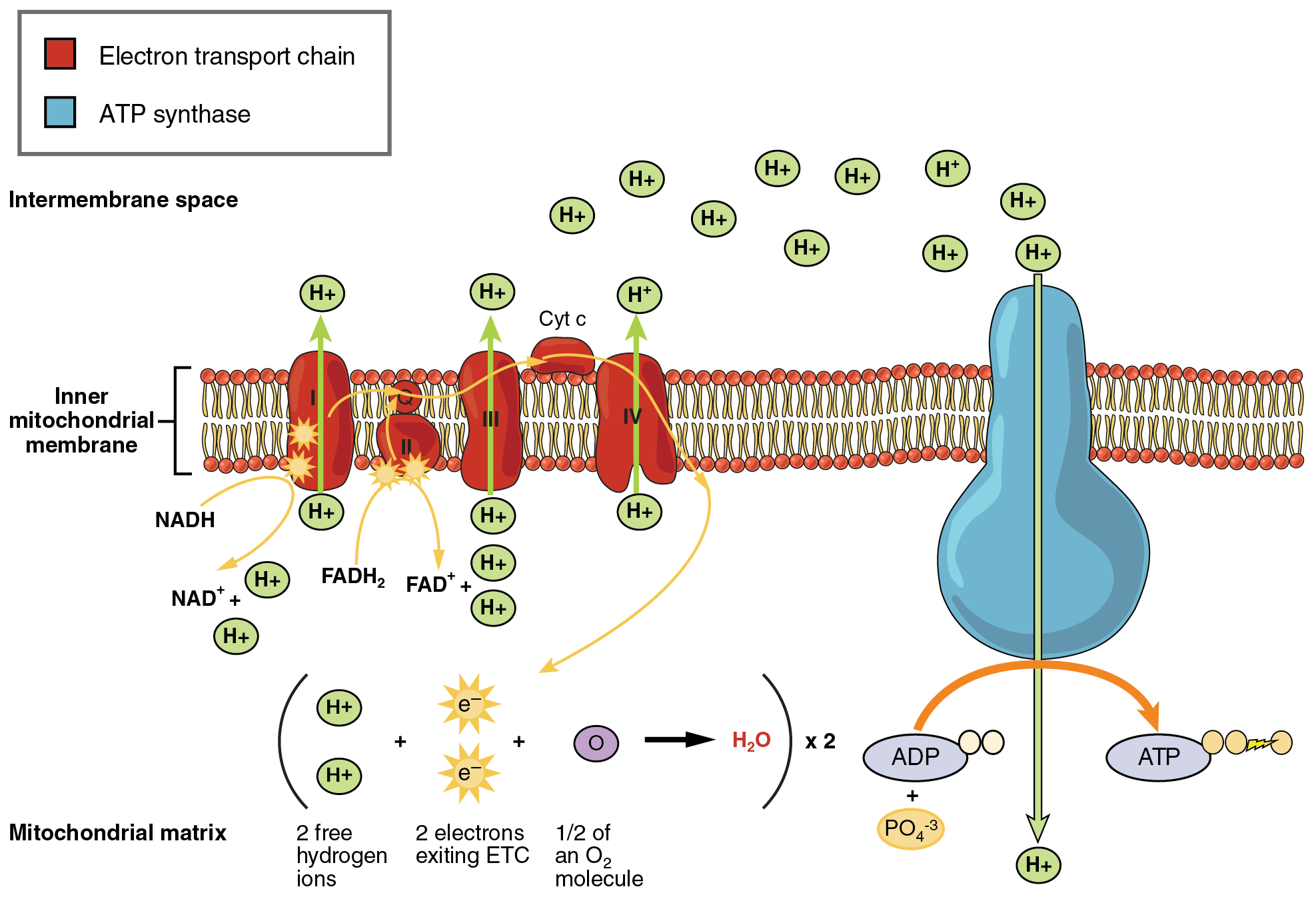
The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
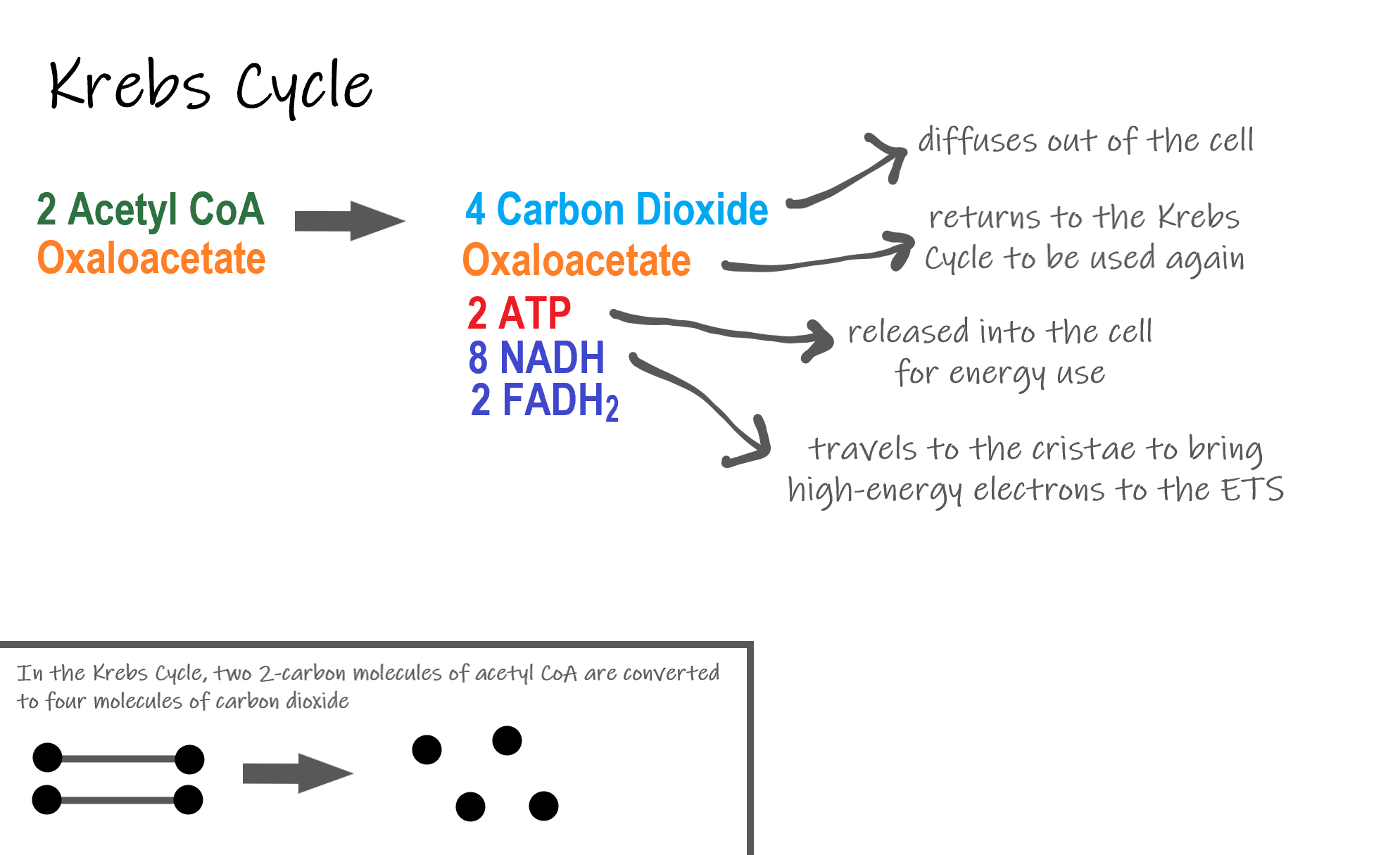
Cellular respiration formula explained. The process of cellular respiration involves many different steps reactions to break down glucose using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide water and energy in the form of ATP. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.
The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. During this activity the students work with a group to discuss the compounds and conditions that need to be present in order. Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes.