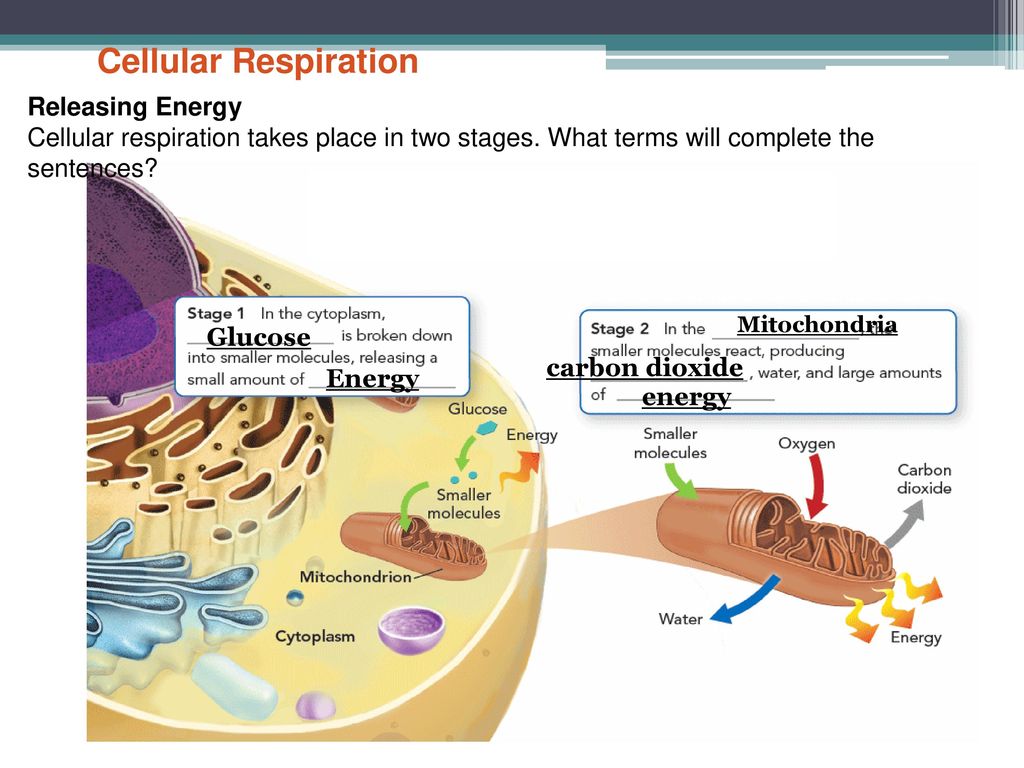
Cellular Respiration Takes Place In Two Stages

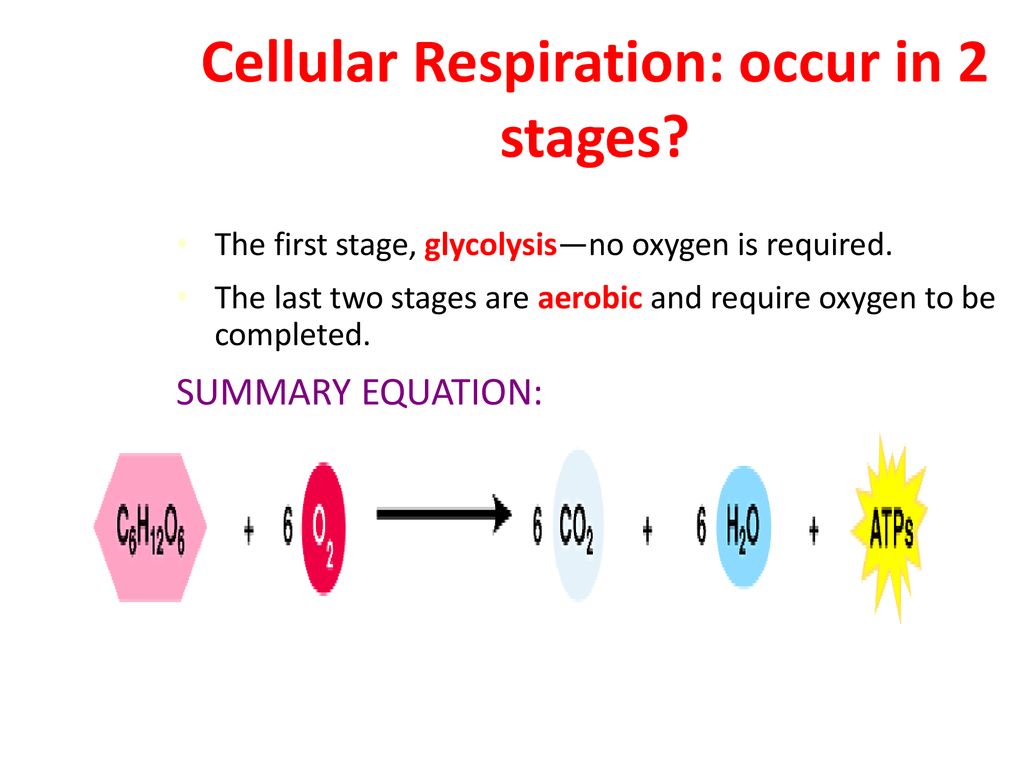
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process.
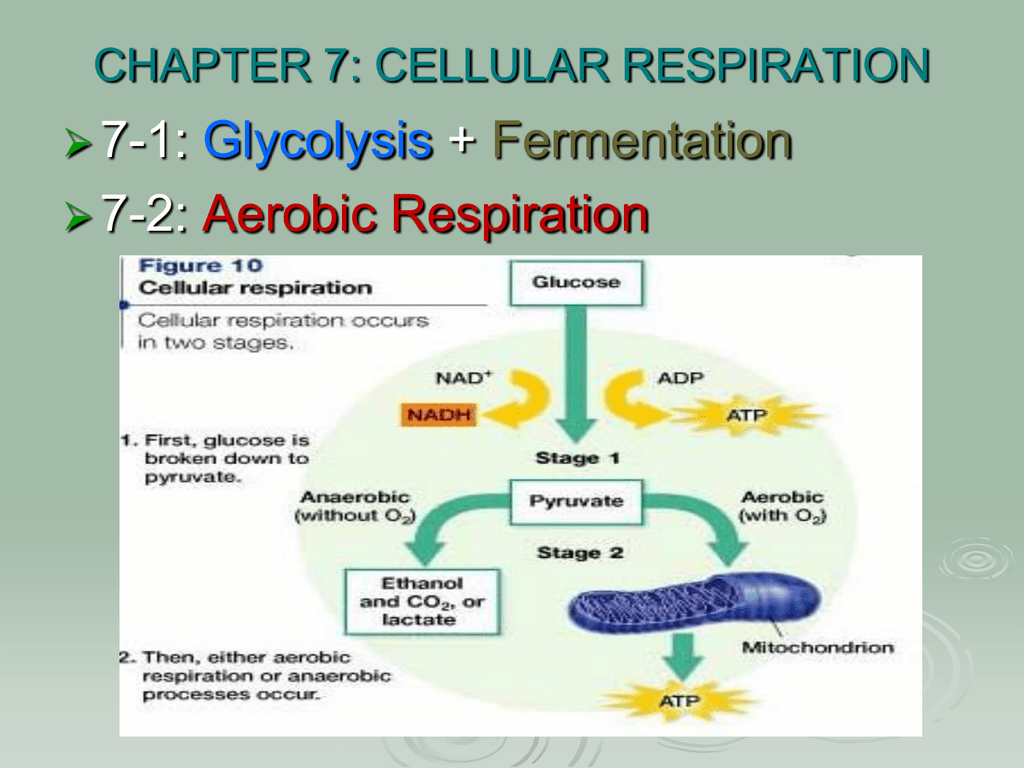
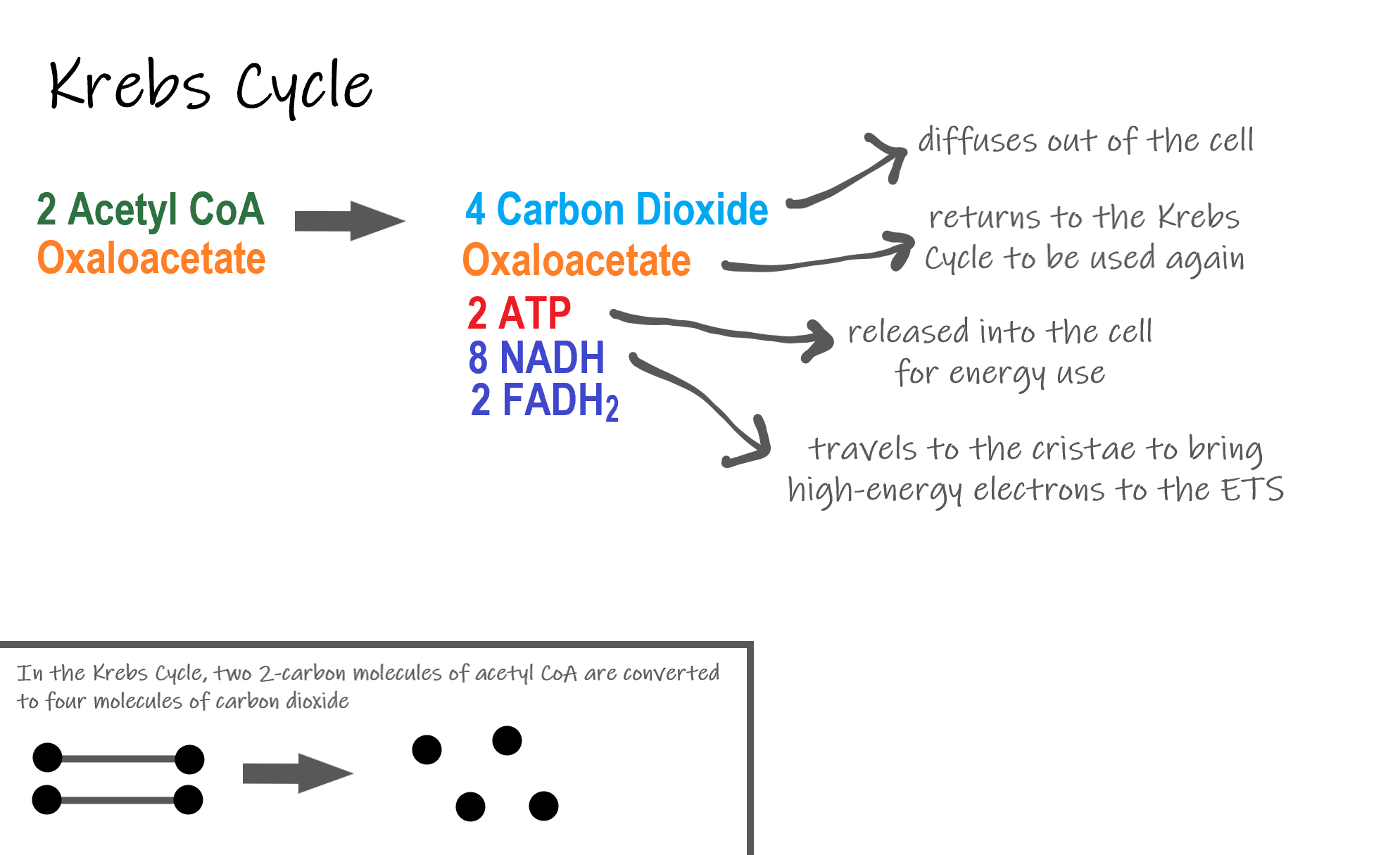
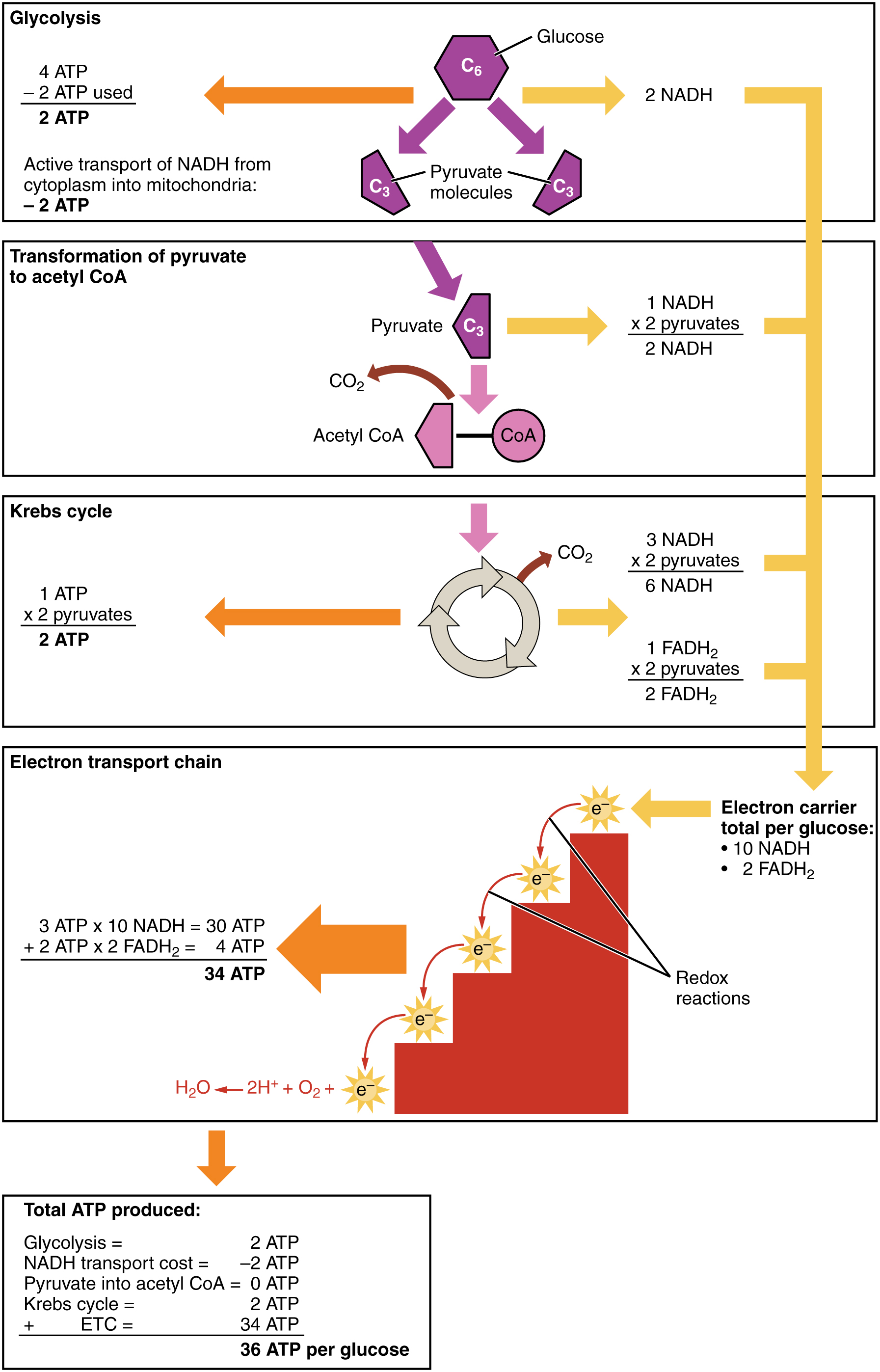
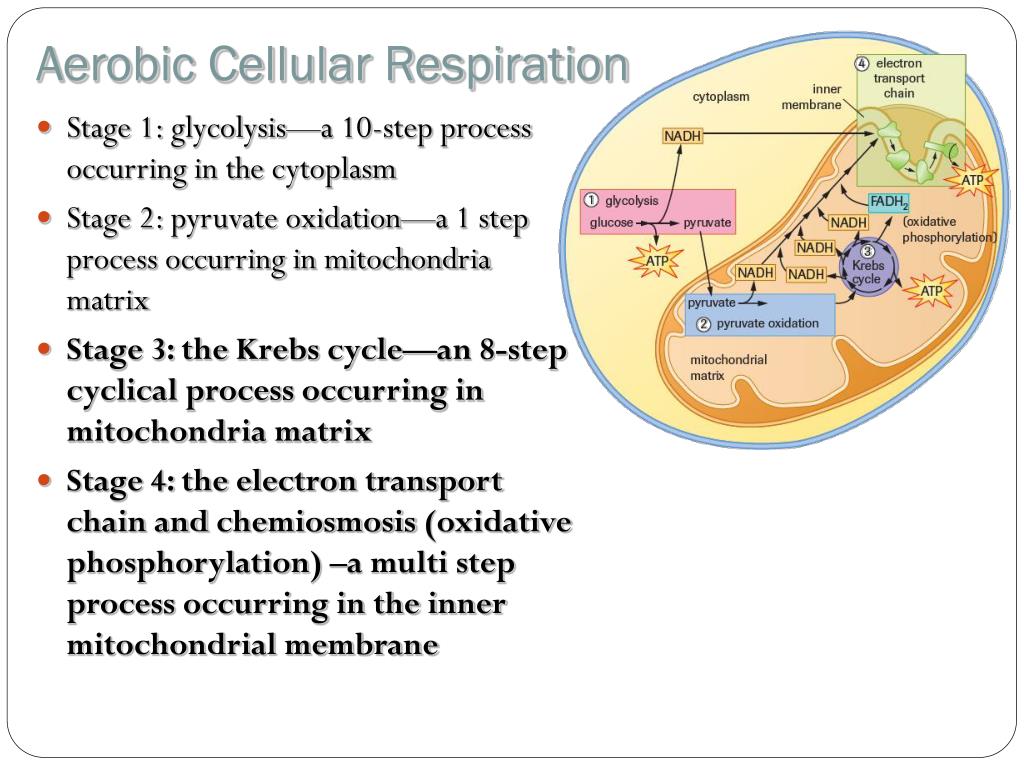
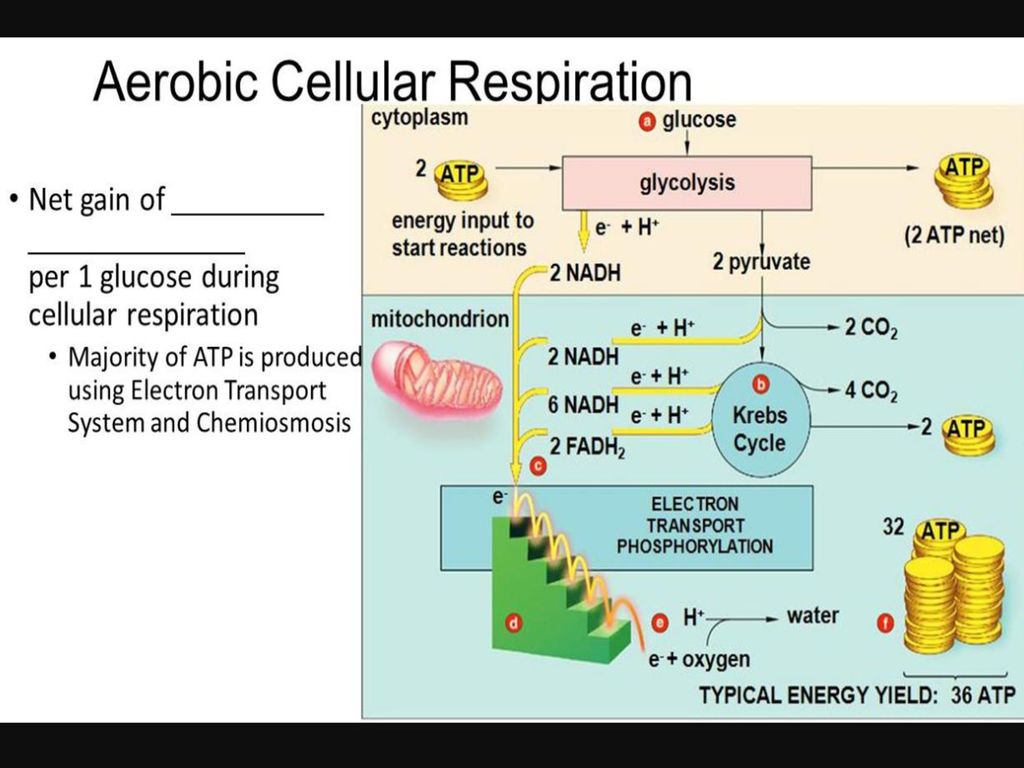
Cellular respiration takes place in two stages. The cellular respiration may be divided into four stages. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into 2 Pyretic Acid Molecules in the Cytoplasm releasing 2 ATP and Hydrogen The Krebs Cycle takes Citric Acid which is a derivative of Pyruvic Acid and converts this through 4 cycles into Hydrogen carbon dioxide and water in the. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
This type of respiration is common in most of the. The net effect is that it splits 6 carbon rings of glucose into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvic acids. Cellular Respiration Equation.
Glycolysis which takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. The stages in anaerobic respiration are. Out of these both internal and cellular respiration occurs at the cellular level.
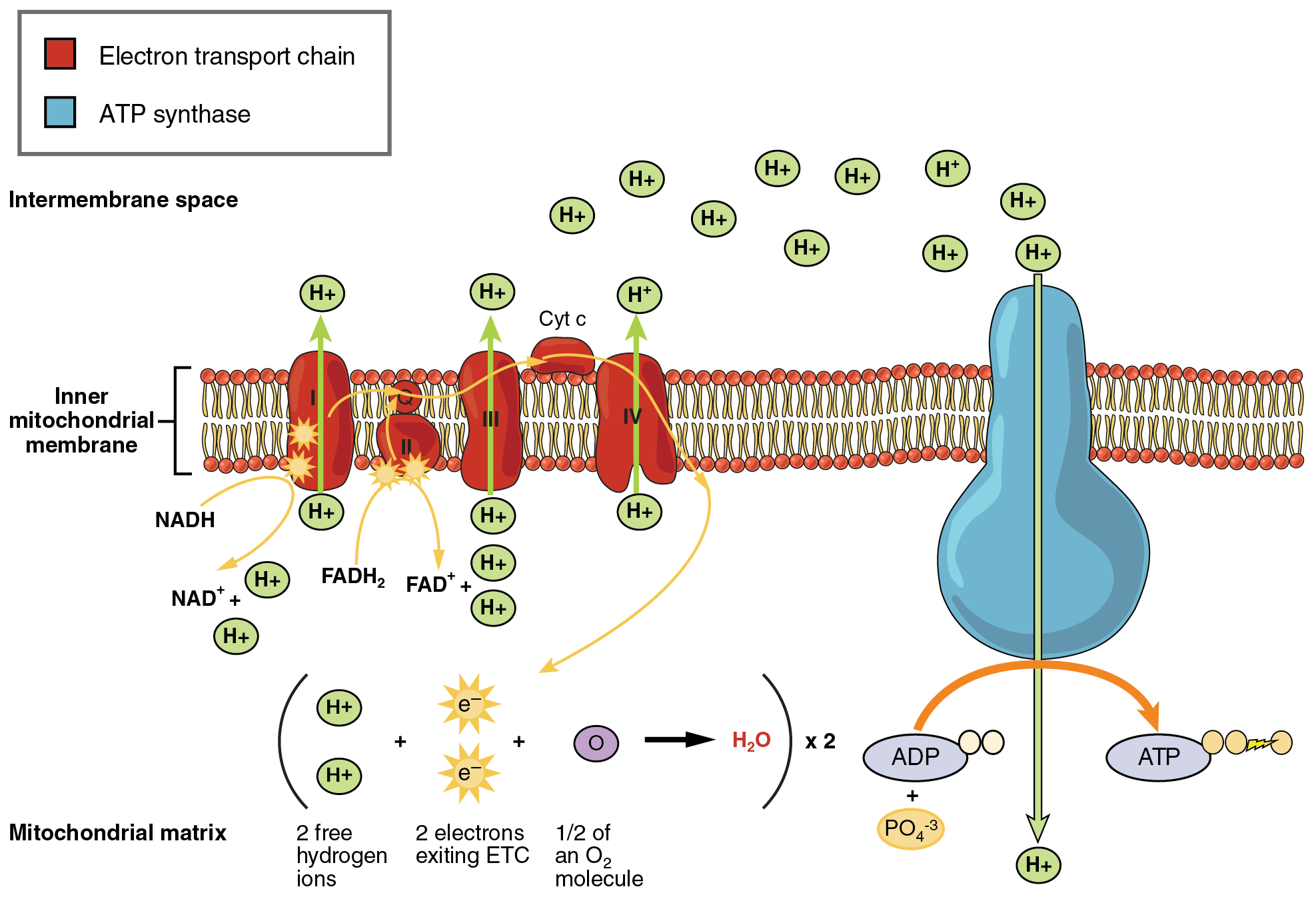
Simultaneously these 3 phases of cellular respiration produce the following number of ATP. Electron transport and oxidative carboxylation. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP.
Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways. Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. The other two stages are aerobic processes.
Used in stage III of cellular respiration electron transport chain to make more ATP. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cell cytoplasm. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm without oxygen.


/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)
