Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

Encourage students to think about adaptations in marine animals related to obtaining food providing camouflage or safety from predators or dealing with changes in temperature salinity pressure lack of sunlight and need for oxygen.
Deep ocean animals adaptations. These creatures have several adaptations like compressible lungs lung-like swim bladders etc to help them overcome the high water pressure in their deep-water environment. The Deep Marine Community Hydrothermal vents. Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive.
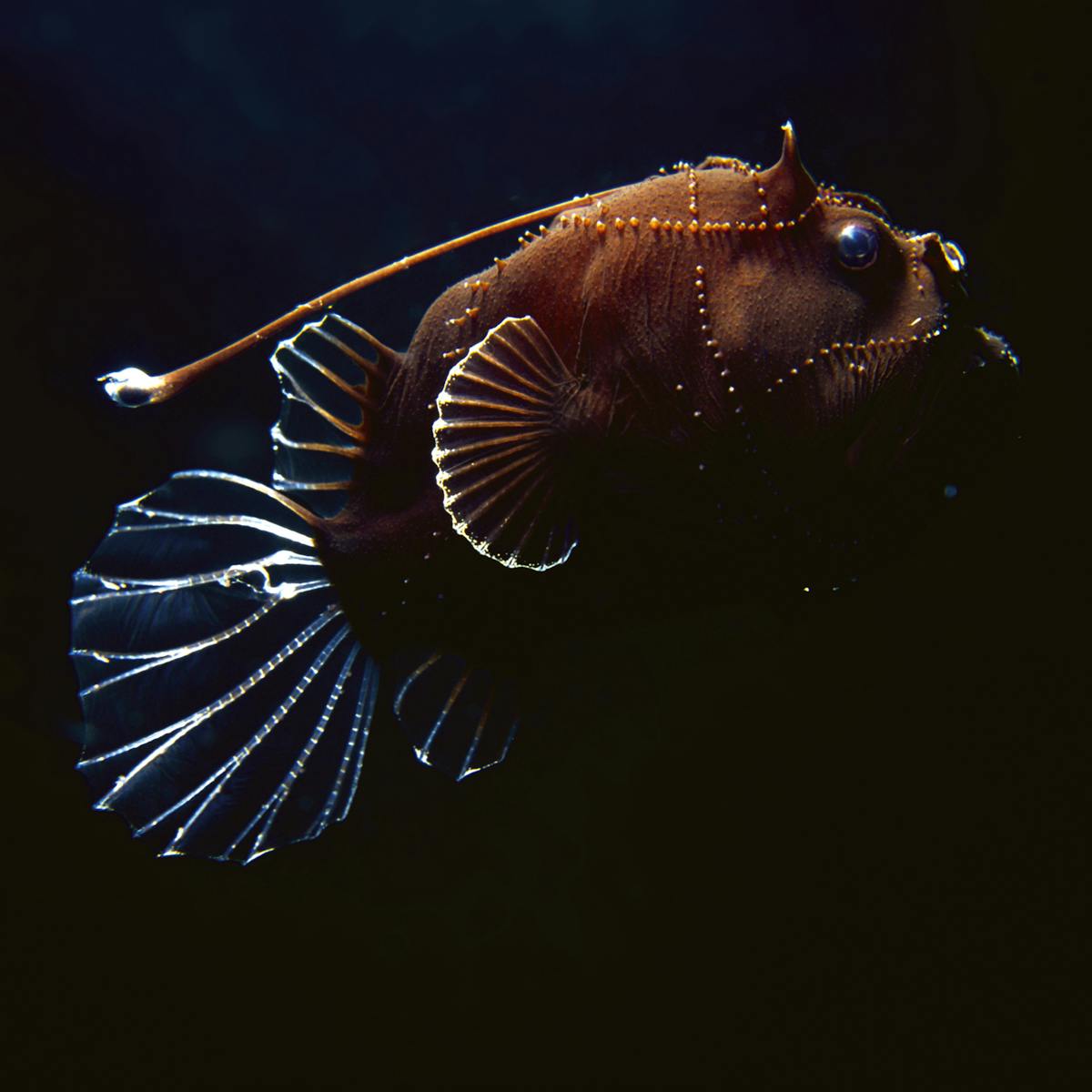
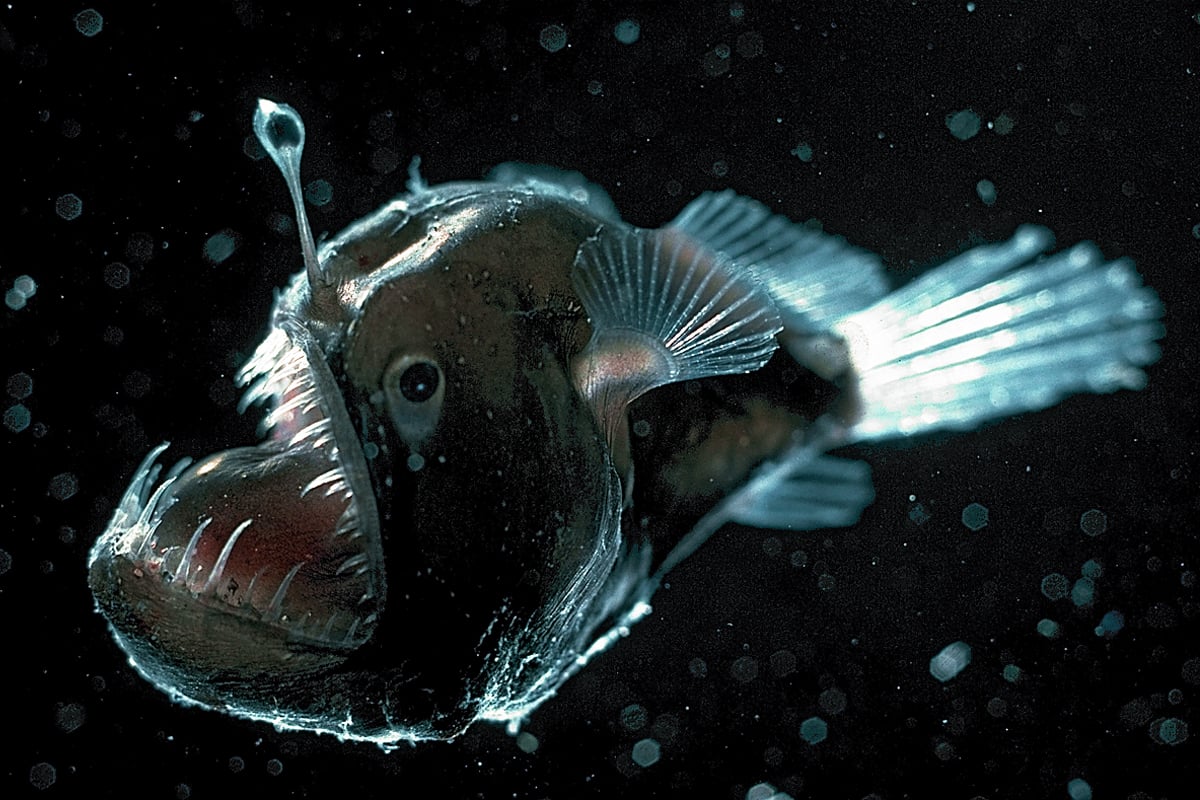
Food is scarce in much of the deep sea in part because photosynthesis only takes place at the oceans surface where theres sunlight. Water depth temperature and the presence or absence of light are some of the conditions that differ in these habitats. Deep Ocean Animal Adaptations These lessons are part of a deep ocean unit.
Enzymes exhibit reduced perturbation of function by pressure membranes have fluidities adapted to deep-sea pressures and temperatures and proteins show. They have strong shells that protect them from wave action drying out and the prying beaks of predators. LS4 - Biological Diversity.
Sharks are very good at finding food. This is often used by animals everywhere for camouflage and protection from predators. Sunlight penetrates here it requires less specialization for seeing.
The dense ocean water is filled with tiny floating organisms. REVIEWS Are there physiological and biochemical adaptations of metabolism in deep-sea animals. Ocean animals have unique adaptations depending on what ocean habitat they live in.
Why are deep sea creatures. They have streamlined bodies to help them swim fast and gills that suck the oxygen out of the water so they can breathe. Many animals such as cockles are adapted to live in these conditions.