Desert Animals Adaptations To Conserve Water

One of the biggest water retention adaptations desert animals have is simply to avoid the sun and extreme heat.
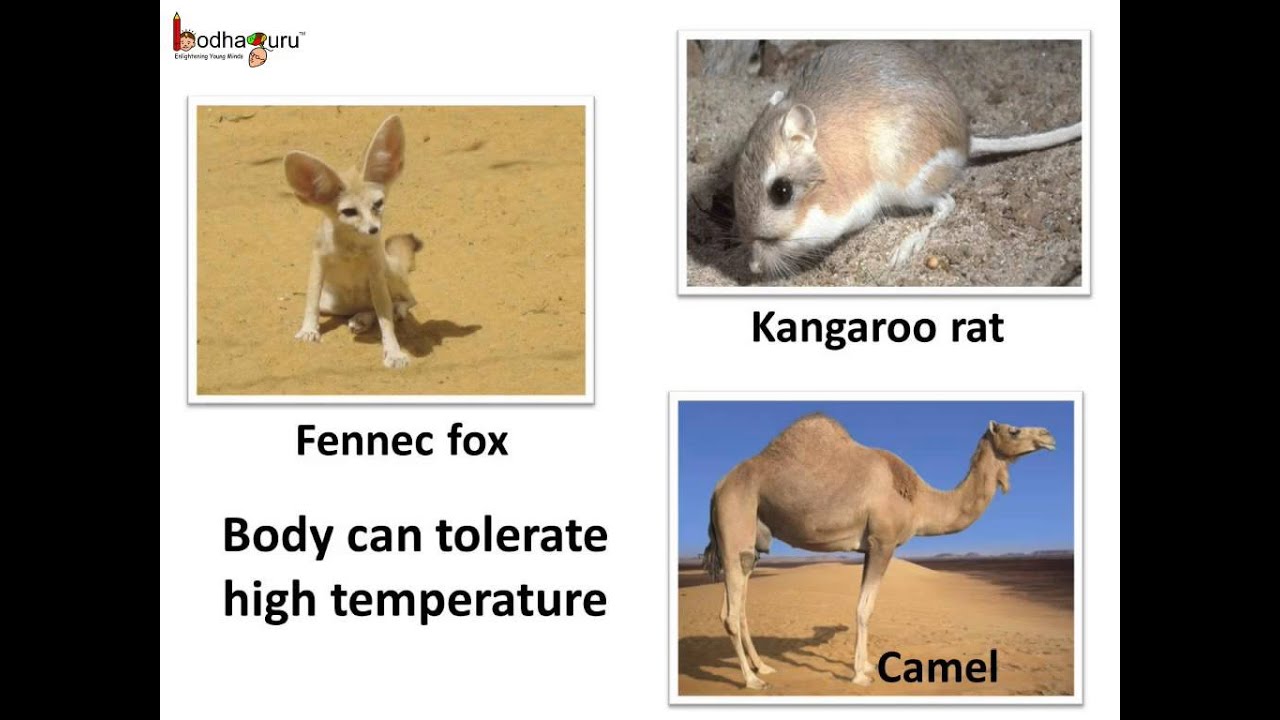
Desert animals adaptations to conserve water. Extreme desert is without any vegetation and rainfall. Plants in deserts have adaptations to conserve water. A common desert adaptation in animals is to save water by not exposing themselves to hot temperatures.
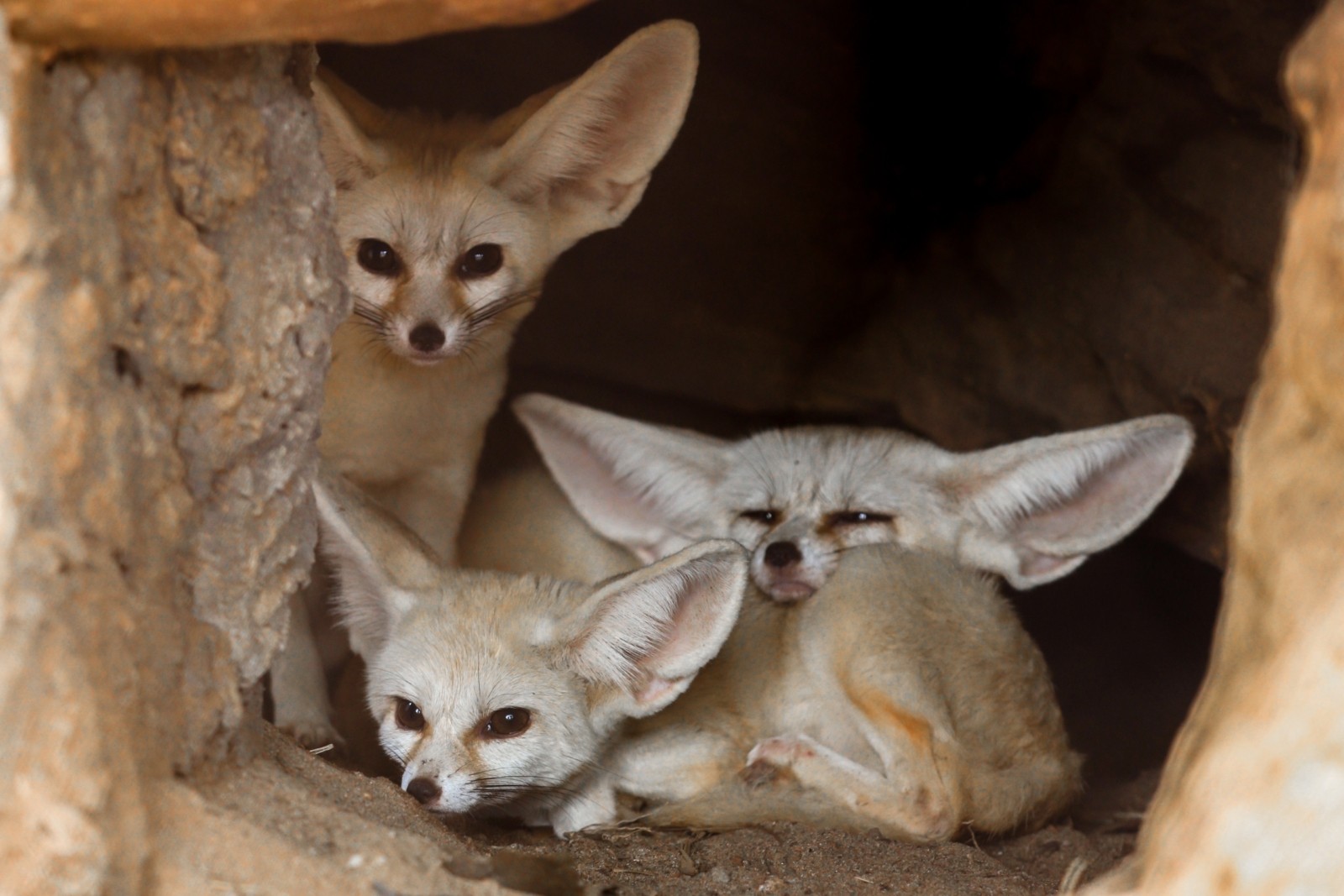
Since water is so scarce most desert animals get their water from the food they eat. Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water. To conserve water they avoid evaporation and concentrate excretions ie.
It gets all the water it needs from eating seeds. To do this they squeeze out every drop available to them and recycle it in their bodies. Camels arent the only animals that.
Cold deserts are also populated by many small mammals that horde food and are stingy about what they eat. Desert animals have developed anatomical and physiological adaptations to keep cool and conserve water. Water is used up in the coolingprocess and can quickly dehydrate even the most water retentive animal so most desert animals have adapted their behavior to avoid getting too hot.
How have animals adapted to the desert. Nocturnal animals avoid activity during the. Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water.
Their extra-long ears help to transfer out excess heat from their body into the air. Adaptations of Desert Plants. All desert animals have learned ways and have adapted themselves either voluntarily or involuntarily to avoid the heat of the desert by simply staying out of it as much as possible.