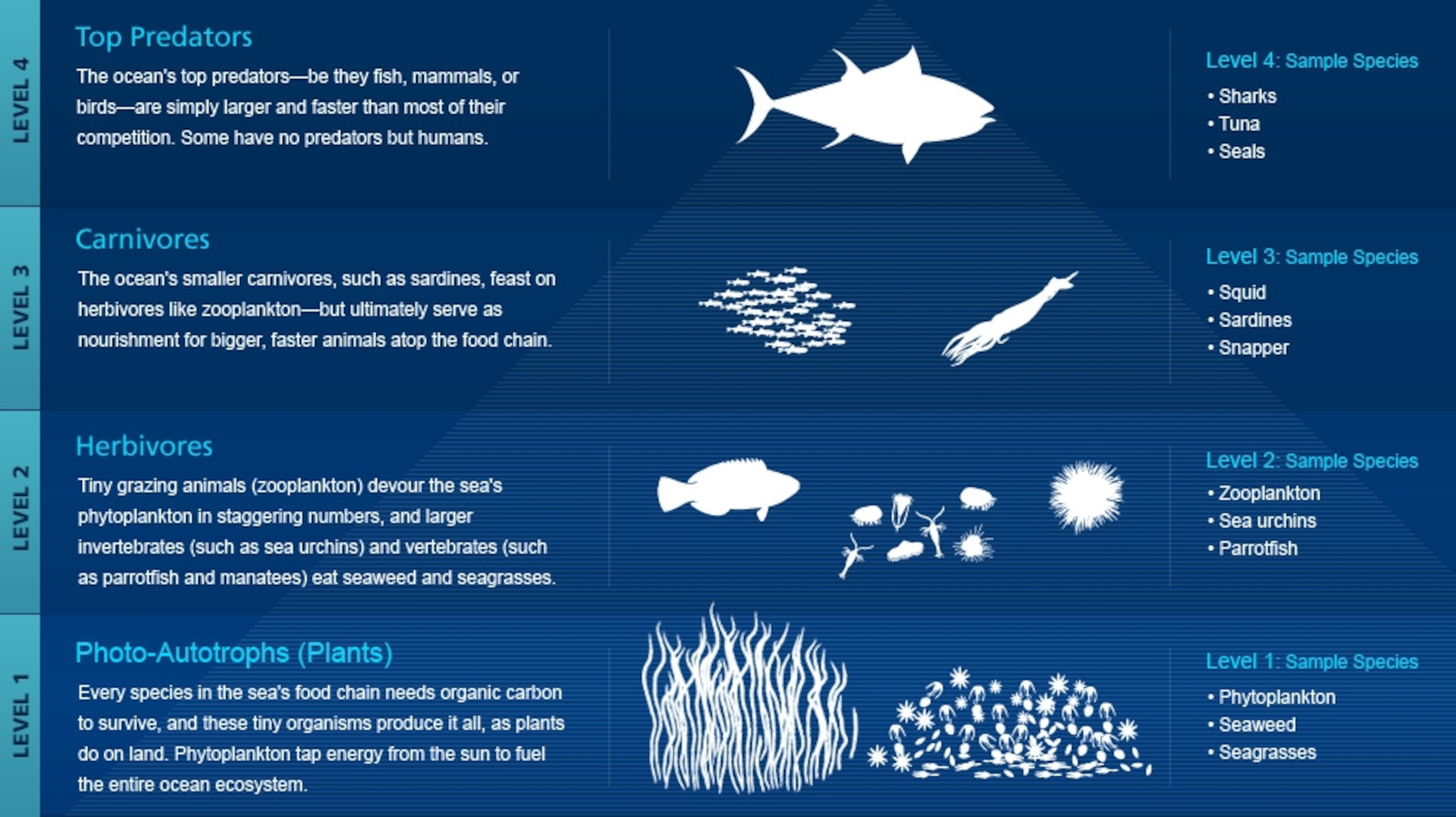
Marine Animals Definition Biology

Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea.
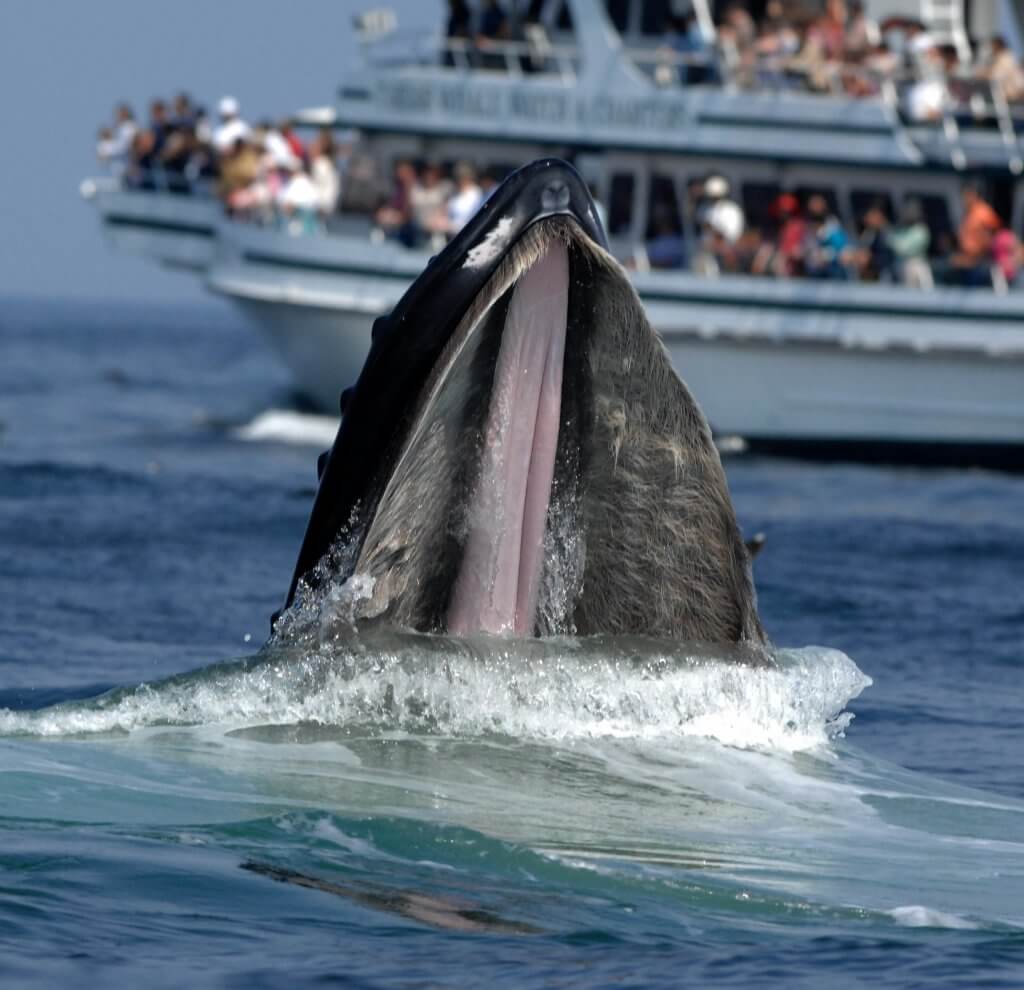
Marine animals definition biology. These organisms take many forms from the tiniest single-celled plankton to the largest animal on Earth the blue whale. Look it up now. Osculum- large opening that lets water out.
Marine biology is the study of marine organisms their behaviors and interactions with the environment. Marine biologists may have many different jobs including working with marine mammals eg a dolphin researcher studying the seafloor researching algae or even working with marine microbes in a lab. Marine life definition biology.
The study of this biome and its components is known as marine biology while the scientists who study marine life are known as marine biologists. Marine biologists study a wide variety of aquatic organisms from microscopic plankton to massive whales. But marine biology is so much more than making a dolphin -- or sea lion -- follow commands.
A marine biologist is someone who is interested in learning and studying marine organisms and what their lives are like in their natural habitats. It also deals with airborne and terrestrial organisms that depend directly upon bodies of salt water for food and other necessities of life. There are a vast array of career choices one can pick from - from studying large ocean animals and what they eat to.
Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth. What is Marine Biology. As a marine biologist you may study a wide range of topics from the behavior physiology and ecology of specific groups of organisms to the interactions between human activity and aquatic environments.
Archaeocytes- cells that move through the sponge. Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge. Spongin- flexible protein fibers.